Introduction to Textile Machinery
Evolution of Textile Machinery
The journey of textile machinery is nothing short of fascinating, illustrating the dynamic interplay between technology and craftsmanship. From the simple handlooms of ancient civilizations to the sophisticated automated machines of today, the evolution of textile machinery reflects significant advancements in engineering and design. In the beginning, textiles were produced manually, with artisans employing basic tools such as spindles and looms. However, the industrial revolution marked a turning point. The invention of the spinning jenny in the 1760s allowed one worker to spin multiple spools of thread simultaneously, drastically increasing production rates. This innovation was pivotal in the textile industry and paved the way for subsequent machinery developments. Over the decades, continual innovations followed: – 1825: The introduction of the power loom revolutionized weaving. – 1870: The Jacquard loom came into play, enabling intricate patterns and designs in fabric. – Late 20th Century: Computerized and automated machines began to emerge, enhancing precision and efficiency. As technology has progressed, so has the complexity of textile machinery. Today, machines are capable of producing specialty textiles for various industries, including fashion, automotive, and geotextiles, showcasing a remarkable blend of artistry and engineering prowess.
Importance of Textile Machinery in the Industry
Textile machinery plays a foundational role in the textile industry. It not only influences the quality of the final product but also affects efficiency, cost, and sustainability. Machinery directly impacts both production times and the ability to meet market demands. Here are a few reasons that highlight its importance:
- Efficiency and Productivity: Modern machines can operate at speeds unimaginable in earlier times. Automated spinning machines, for example, can produce hundreds of kilometers of yarn daily, significantly boosting productivity.
- Quality Control: Advanced technology enables precise control over production processes, ensuring that textiles meet high-quality standards. Consistent yarn thickness, dye precision, and fabric strength can be achieved with today’s machinery.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial investment in textile machinery can be substantial, the long-term savings through reduced labor and material wastage make it a financially sound choice for manufacturers.
- Innovation and Trends: With consumer preferences constantly evolving, textile machinery allows for quick adaptation to new trends. For instance, demand for sustainable fabrics has driven innovations in recycling and eco-friendly production methods.
- Global Competitiveness: In an increasingly global market, the efficiency and advanced capabilities of textile machinery enable companies to maintain competitiveness on an international scale.
In summary, the evolution of textile machinery showcases a remarkable transformation that continues to shape the textile industry today. By marrying technological advancements with traditional craftsmanship, textile machinery is not just a tool but a critical component of the sector’s growth and sustainability. With continuous innovation, the future of textile machinery promises even more exciting developments, setting the stage for the ongoing evolution of textiles.

Spinning: The Heart of Textile Production
As we delve deeper into the various stages of textile production, one cannot overlook the critical role of spinning. It is often regarded as the heart of textile production, as it transforms raw fibers into yarns, which serve as the foundation for fabrics. Understanding this process sets the stage for comprehending the broader textile manufacturing landscape.
Understanding the Spinning Process
The spinning process involves several intricate steps that collectively convert fibers into usable yarn. This transformation is essential because the quality of the yarn directly impacts the final fabric’s characteristics, such as strength, texture, and appearance. Here’s a basic overview of the spinning process:
- Fiber Preparation: Raw fibers, whether from natural sources like cotton or synthetic materials like polyester, are first cleaned and arranged. This step may involve carding, which opens and separates tangled fibers.
- Drafting: Once prepared, the fibers are drawn out to align them into a strand. This process increases the length of the yarn while reducing its thickness, thus ensuring consistency.
- Twisting: The drafted fibers are then twisted together. This is crucial as twisting adds strength to the yarn, preventing it from breaking during subsequent processes.
- Winding: Finally, the spun yarn is wound onto spools or cones for easy handling and transport to weaving or knitting stages.
Each step in this process must be executed with precision to ensure high-quality yarn, showcasing how important spinning is to textile production.
Types of Spinning Machines
Different spinning machines are designed to cater to varied types of fibers and desired yarn characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
- Ring Spinning Machines:
- The most widely used, it produces high-quality yarn with good strength.
- Uses a rotating ring that guides the yarn during the twisting process.
- Open-End Spinning Machines:
- Faster and more economical than ring spinning.
- Produces less refined yarn, ideal for textiles requiring bulk.
- Air Jet Spinning Machines:
- Employs air to twist the fibers together, resulting in lighter and softer yarns.
- Suitable for specialized applications, such as high-performance fabrics.
- Vortex Spinning Machines:
- Uses a vortex to create a unique structure in the yarn, providing a distinct feel.
- Ideal for creating twist-free yarns with even strength.
Exploring the spinning process and the various types of spinning machines highlights the incredible technology that underpins textile production. Understanding these machinery specifics empowers manufacturers to choose the right equipment for their production needs, significantly impacting the overall quality of the end product. In conclusion, spinning lies at the core of textile production. With the right spinning techniques and machinery, manufacturers can produce an array of yarns, each serving a unique purpose in the creation of textiles that fulfill consumer needs and trends.

Weaving: Transforming Yarn into Fabric
As we delve into the intricate world of textile production, we find ourselves at a crucial juncture: weaving. This process is not just about creating fabric; it embodies a rich history and showcases the artistry that combines technology and craftsmanship. The art of weaving is a fascinating blend of tradition and innovation, where each lesson learned over centuries is woven into the fabrics of today.
The Art of Weaving
At its core, weaving is the process of interlacing yarns or threads to create fabric. This interlacing is akin to a dance, where each thread moves in harmony with the others to produce a coherent piece of artwork. Some might recall the sight of a loom in action, with skilled hands deftly manipulating the shuttle that carries the yarn. Weaving has an emotional resonance; it tells stories through patterns, colors, and textures. For instance, in many cultures, certain designs and colors symbolize heritage, community, and even spirituality. Weaving has the power to evoke feelings of nostalgia and belonging, as personal stories can be stitched into the very fabric of our clothing. Techniques vary, allowing for diverse fabric types, from delicate silk to sturdy denim. The process can be both machine-operated and manually crafted, highlighting the blend of technology with human creativity.
Different Types of Weaving Machines
The machines designed for weaving are as diverse as the fabrics they produce. Each type of weaving machine has its characteristics and applications, catering to different market demands. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Handlooms:
- Often used for artisanal and small-scale production.
- Allows weavers to have total control over the weaving process, which can result in unique and high-quality textiles.
- Shuttle Looms:
- Utilize a shuttle to transport the cross-thread (weft).
- Known for their speed and efficiency, they are commonly used in mass production.
- Rapier Looms:
- Employ a rapier to carry the weft yarn across the warp threads.
- They can create a wide variety of fabrics, from lightweight to heavy textiles.
- Jacquard Looms:
- Equipped with a Jacquard head enabling intricate weaving patterns (like brocades and damasks).
- They are computer-controlled and can produce complex designs with ease.
- Air Jet Looms:
- Utilize compressed air to insert the weft yarn, allowing for high-speed weaving.
- Ideal for large production runs and can handle diverse material types.
The variety of weaving machines showcases the continuous evolution of textile production technology, each contributing to a vast array of fabric possibilities. Whether through tradition or technological advancement, weaving remains a key pillar in textile manufacturing. Understanding the nuances of weaving not only appreciates the fabric’s beauty but also the craftsmanship and technology that bring it to life. As we transition to the next chapter—knitting—let’s keep in mind how these processes collectively influence the industry, continually pushing the boundaries of creativity and functionality in textiles.

Knitting: Creating Textiles with Needles
As we transition from the weaving process, it’s time to explore another major technique in textile production: knitting. While weaving relies on interlacing yarns, knitting is all about creating loops that form a flexible fabric. This method not only adds variety to the types of textiles available today, but it also allows for unique designs and patterns that cater to various markets, from fashion to home decor.
Overview of the Knitting Process
The knitting process may appear simple at first glance, but it involves a series of intricate steps that transform yarn into fabric. Here’s a closer look at how it works:
- Yarn Preparation: Much like weaving, the quality of the yarn significantly influences the end product. Professionals typically source high-quality fibers, whether they come from natural sources like wool or synthetic materials.
- Creating the Knitting Structure: Knitting can be done by hand or machine. The traditional hand knitting involves using two needles where the knitter manually creates each loop. In contrast, machine knitting uses sophisticated equipment to automate the process, producing consistent patterns with high efficiency.
- Stitch Types: Different stitch techniques—like garter stitch, ribbing, or cable—affect both the texture and appearance of the fabric. The flexibility of knitting allows for creativity and experimentation.
- Finishing Touches: After knitting, the fabric often undergoes a finishing process, which may include washing, blocking, or even dyeing to enhance its quality and appearance.
This process results in various end usages: clothing, accessories, and more—each piece carrying the unique fingerprint of its creation.
Types of Knitting Machines
When it comes to knitting machinery, the landscape is diverse, catering to many different aspects of textile production. Here are some common types of knitting machines:
- Flat Knitting Machines:
- Ideal for producing flat pieces of fabric.
- Widely used in making garments like sweaters.
- The mechanism moves back-and-forth, enabling the creation of panels.
- Circular Knitting Machines:
- These machines create seamless tubes of fabric and are particularly popular for jersey fabrics.
- Suited for producing hosiery and t-shirts.
- Operate in a continuous cycle, making them highly efficient.
- Warp Knitting Machines:
- Produce fabrics by interlocking loops in a vertical direction.
- Used predominantly for laces and mesh fabrics.
- Known for their strength and stability.
- Computerized Knitting Machines:
- Incorporate advanced technology, allowing for intricate designs and patterns.
- These machines can be programmed for precision, reducing manual labor significantly.
- Industrial Knitting Machines:
- Designed for mass production, they achieve rapid output without compromising quality.
- Commonly found in larger textile manufacturing units.
As technology advances, the knitting industry continues to innovate. With automated solutions, the traditional art of knitting is being redefined, making it both an efficient and intricate component of textile production. The blend of craftsmanship and machinery ensures that diverse designs and superior quality remain at the forefront of textile offerings. Delving into knitting reveals not just the complexity behind fabric creation but also the endless creative possibilities it offers—a testament to the ever-evolving textile industry.

Continuing from the previous discussion on knitting, we now delve into the vibrant world of dyeing and printing, essential steps in the textile manufacturing process that breathe life into fabric. Adding color and design is not merely an aesthetic choice; it’s a way to create textiles that resonate with consumers’ preferences and textile trends.
Techniques in Textile Dyeing
Dyeing techniques have evolved significantly over the years, ranging from traditional methods to more sophisticated approaches that prioritize both efficiency and environmental responsibility. Here are some of the most notable dyeing techniques:
- Batch Dyeing: This technique involves dyeing a specific batch of fabric in one go. It’s common for smaller runs and allows for rich, uniform color application. A personal anecdote highlights its charm; a local artisan in my town uses this method to produce custom colorful scarves that boast unique dye patterns.
- Continuous Dyeing: For large-scale production, continuous dyeing methods are employed. Fabric is fed through a dyeing machine, allowing for quick and efficient dye application. This method maintains high productivity while ensuring consistent color.
- Digital Dyeing: This innovative technique is taking the industry by storm. Digital printing on textiles involves the use of inkjet technology, enabling intricate designs and color variations directly onto fabric. It allows for customization at unprecedented levels and minimal waste, which is a significant advantage for designers.
- Eco-Friendly Dyeing: With growing environmental concerns, many manufacturers are turning to synthetic dyes made from natural sources, such as plants and minerals. These eco-friendly dyes are not only safer for the environment but also produce vibrant colors.
Each technique varies in application and suitability, depending on the desired outcome and fabric type.
Innovations in Textile Printing
In addition to dyeing, textile printing has seen remarkable technological advancements that enhance creativity and sustainability. Here are some key innovations:
- Digital Printing: Much like digital dyeing, digital printing technology uses large format inkjet printers to apply designs onto fabrics. This method not only allows infinite design possibilities but significantly reduces water and chemical usage when compared to traditional screen printing methods.
- 3D Printing: An exciting frontier in textile production, 3D printing is transforming fabric creation. Designers can create intricate textures and patterns that are difficult to achieve with conventional methods. It opens up a world of possibilities for custom fashion apparel.
- Sustainable Inks: The shift toward environmentally friendly practices also includes the development of inks derived from natural sources. These inks ensure that the designs are not only vivid but also biodegradable, a crucial step toward reducing the textile industry’s carbon footprint.
- Reflective and Photochromic Printing: These innovative printing methods allow fabrics to change appearance based on light exposure, adding an interactive element to clothing. Imagine a shirt that changes color as the sun moves—this kind of technology captures consumer interest and embraces creativity.
As the textile industry continues to innovate in dyeing and printing, it paves the way for more responsible and exciting future developments in textile design, ensuring that new fabrics not only look great but also contribute positively to the environment. The advances in these areas demonstrate the industry’s commitment to balancing aesthetics with sustainability—an effort that benefits both consumers and the planet.

Finishing: Enhancing the Quality of Textiles
As the process of textile manufacturing reaches its pinnacle, the finishing stage plays a crucial role in determining the fabric’s quality and functionality. Imagine having a beautifully woven textile that lacks that vibrant color or softness we desire; that’s where finishing comes in. The finishing process not only brings textiles to life but also sets them apart in an ever-competitive market.
Importance of Textile Finishing
Textile finishing is vital for several reasons:
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Finishing treatments can add luster, softness, and an appealing appearance to fabrics. Techniques such as mercerization and resin finishes greatly improve visual appeal.
- Improved Functionality: Certain finishing processes endow textiles with specific functionalities, such as water resistance, flame retardancy, and moisture management, making them suitable for various applications.
- Durability: Proper finishing can significantly extend the life of a fabric. Techniques like sanforizing prevent shrinkage and maintain dimensional stability, ensuring that a garment retains its shape over time.
- Comfort: Finishing processes, including softening, enhance the feel of the fabric against the skin, drastically improving comfort levels for the end-user.
For instance, the way a cotton t-shirt feels to wear can be a result of different finishing techniques. Imagine wearing a stiff shirt versus one that has undergone a softening process. There’s no contest when it comes to comfort!
Modern Finishing Machinery
With advancements in technology, modern finishing machinery has revolutionized the way textiles are treated. Gone are the days of labor-intensive processes; today’s finishing machines are efficient, versatile, and smart. Some prominent types of modern finishing machinery include:
- Calendar Machines: These are used to produce a smooth, glossy finish on various fabrics. They work by compressing textile layers through heavy rollers, creating a sleek look.
- Coating Machines: Ideal for applying protective coatings that enhance durability and functionality, such as water-resistant finishes.
- Heat Setting Machines: These machines set the fabric’s dimensions while enhancing its physical properties. Synthetic fabrics often benefit from this process as it eliminates any stress and stabilizes the fiber.
- Dyeing and Finishing Range: A multi-functional machine that can carry out both dyeing and finishing operations simultaneously. This not only saves time but also improves energy efficiency.
Modern finishing machinery comes equipped with automatic controls, reducing human error and optimizing processes, resulting in:
- Higher Production Rates: Advanced technology often ensures a quicker turnaround time without compromising quality.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Enhanced machine efficiency leads to lower operational costs and minimizes waste.
- Diverse Applications: The adaptability of these machines to handle multiple types of fabrics allows manufacturers to cater to a wide array of market needs.
In summary, textile finishing is more than just a final step; it is a critical phase that enhances quality and marketability. As the industry continues to evolve with technology and innovation, the finishing process will play an even more significant role in defining the fabrics of the future.

Automation in Textile Production
As the textile industry continues to evolve, automation has emerged as a game-changer, ushering in advancements that significantly enhance efficiency, quality, and productivity. With the integration of automated processes, manufacturers can streamline operations and adapt to the ever-changing market demands.
Role of Automation in Textile Industry
Automation plays a crucial role in the textile industry by transforming traditional manufacturing methods into more efficient, controlled, and reliable systems. This shift is not just about speed; it’s about precision and consistency too. For instance, consider a weaving factory where traditional machines require manual setups for various fabric types. With automation, specialized machines can automatically adjust settings based on fabric specifications, which not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of human error. Key roles of automation in the textile industry include:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated machines can operate continuously, allowing for higher production rates without fatigue.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Precision machinery minimizes defects and ensures uniformity in textile products.
- Real-time Monitoring: Automated systems offer real-time monitoring, making it easier to manage production processes and detect potential issues early.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Automation collects valuable data that can help managers make informed decisions regarding production processes, resource allocation, and quality control.
From spinning to weaving and dyeing, automation enhances every step of the textile production process.
Advantages of Automated Textile Machinery
The shift towards automation brings several clear advantages, positioning textile businesses for long-term success. Some of these advantages include:
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in automated machinery may be significant, the reduction in labor costs and waste leads to considerable savings over time.
- Faster Production: Automated systems can complete tasks much more quickly than manual labor, allowing businesses to meet tight deadlines and high demand without sacrificing quality.
- Improved Safety: Automation often removes workers from hazardous tasks, reducing the likelihood of workplace accidents, and creating a safer environment.
- Consistency in Quality: Automated machinery delivers consistent results, minimizing variations that can occur with manual operations.
- Flexibility: Modern automated machines often allow for quick changes in production types, enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to market trends or consumer preferences.
Summary Table of Automation Benefits| Advantage| Description|
|——————————-|———————————————————| | Cost Savings| Reduction in labor costs and material waste| | Faster Production| Higher output rates to meet market demands| | Improved Safety| Less exposure to hazardous tasks for workers| | Consistency in Quality| Minimization of variations in product quality| | Flexibility| Quick adjustments to production settings are possible| In conclusion, the role of automation in the textile industry cannot be overstated. It not only drives efficiency but also ensures that manufacturers are equipped to meet contemporary challenges. As technology continues to advance, those who embrace automation will likely find themselves at the forefront of the textile sector, ready to capitalize on new opportunities.

Sustainable manufacturing practices have taken center stage in the textile industry as companies and consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with traditional textile production methods. As we explore this vital topic, let’s delve deeper into the green initiatives that are making waves in textile machinery and the innovative production methods that promote sustainability.
Green Initiatives in Textile Machinery
Textile machinery manufacturers are stepping up to the challenge of sustainability by innovating and integrating eco-friendly technologies into their production lines. A few notable green initiatives include:
- Energy Efficiency: Modern textile machines are designed to consume less energy. For instance, some spinning machines are now equipped with advanced drive systems that utilize energy-efficient motors, significantly reducing electricity consumption.
- Water Conservation: Dyeing remains one of the most water-intensive processes in textile manufacturing. However, recent machinery innovations utilize water-saving techniques, such as closed-loop systems. These systems recycle water, reducing overall consumption by as much as 90%.
- Use of Sustainable Materials: Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating bio-based materials into machinery production. Instead of traditional plastics, some are utilizing biodegradable polymers, reducing plastic waste.
- Pollution Reduction: Anti-pollution technologies are integrated into machines to treat effluents before they are discharged. This results in lower emissions of harmful substances into the environment.
Having witnessed the implementation of these technologies first-hand in a local textile factory, it’s remarkable how such machinery can not only reduce operational costs but also benefit the environment significantly.
Sustainable Textile Production Methods
Beyond machinery, sustainable practices in textile production encompass various methods that minimize environmental impact:
- Organic Cotton and Natural Fibers: Using organic cotton and natural fibers like hemp and bamboo reduces the reliance on pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, promoting a cleaner ecosystem.
- Eco-Friendly Dyeing: Innovations in dyeing technology, such as digital printing, allow for precise color application, reducing dye waste. Additionally, natural dyes made from plant-based materials provide a sustainable alternative to chemical dyes.
- Recycling and Upcycling: Many companies are embracing circular economy principles by recycling post-consumer textile waste into new garments or upcycling them into new products. For instance, denim manufacturers are repurposing old jeans into new styles, thereby minimizing waste.
- Fair Trade Practices: Sustainability extends beyond environmental aspects to include ethical production. Fair trade practices ensure that garment workers receive fair wages and safe working conditions. This holistic approach to sustainability contributes positively to local communities.
By integrating these sustainable practices in textile manufacturing, the industry not only mitigates its environmental footprint but also embraces a future that prioritizes ethical and responsible production. Transitioning to these methods may involve investment and time, but the long-term benefits for both the planet and industry stakeholders are undeniable. As the textile industry continues on its path towards sustainability, stakeholders—including consumers—may find great satisfaction in supporting brands that prioritize eco-friendly and ethical practices.

Maintenance and Care of Textile Machinery
When it comes to textile machinery, ensuring proper maintenance can significantly prolong the life of your equipment while enhancing its performance. Just like a car needs regular servicing to run smoothly, textile machines also require dedicated care and attention.
Tips for Maintaining Textile Equipment
Maintaining textile machinery may seem daunting, but with the right strategies in place, the process can be manageable and effective. Here are some essential tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and lint can accumulate in machinery, leading to reduced efficiency. Regularly clean areas around spindles, filters, and any moving parts to prevent build-up.
- Lubrication: Just as athletes rely on proper shoes to avoid injury, machinery depends on lubrication to function effectively. Use the recommended lubricants for each machine to minimize friction and wear.
- Routine Inspections: Establish a schedule for thorough inspections. Look for signs of wear and tear, such as frayed belts or unusual noises. Tackling issues early can prevent costly breakdowns.
- Calibration Checks: Equipment may drift from its calibrated settings over time. Routine checks will ensure that machinery operates within specified parameters, delivering high-quality output consistently.
- Staff Training: Ensure that all operators are well-trained in handling machinery correctly. Knowledgeable staff can spot potential issues early and take corrective actions before they escalate.
- Documentation: Keep a maintenance log for each piece of equipment. Documenting services performed and any issues encountered helps spot patterns and predict maintenance needs.
Common Issues and Solutions in Textile Machinery
Despite vigilant maintenance, textile machinery may still encounter problems. Here are some common issues that arise and practical solutions to address them:
- Thread Breakage: This is a frustrating issue and can significantly slow production.
- Solution: Check tension adjustments and ensure the correct thread type and size are being used. Clean the bobbin area regularly to avoid lint accumulation.
- Misalignment of Components: Misalignment can lead to inefficient operation and wear out parts quicker.
- Solution: Use alignment tools to ensure all components are set correctly. Regular checks during maintenance can help immediately identify misalignments.
- Motor Overheating: Overheated motors can lead to devastating breaks.
- Solution: Ensure that cooling systems are functioning well, and avoid overloading machines. Clean the cooling vents to maintain airflow.
- Stitch Quality Issues: Inconsistent stitching can result in product defects.
- Solution: Monitor needle wear and replacement schedules. Also, check the fabric tension and feed rate to ensure consistency.
- Vibration in Machines: Excessive vibrations can cause misalignment and lead to machine failure.
- Solution: Check for loose bolts and connections. Additionally, consider adjusting the feet of the machine to stabilize it.
By implementing these tips and being aware of common issues, operators can ensure their textile machinery runs smoothly and efficiently. A little effort in maintenance not only extends the life of the machines but also enhances the overall quality of the final products, keeping the textile business thriving.
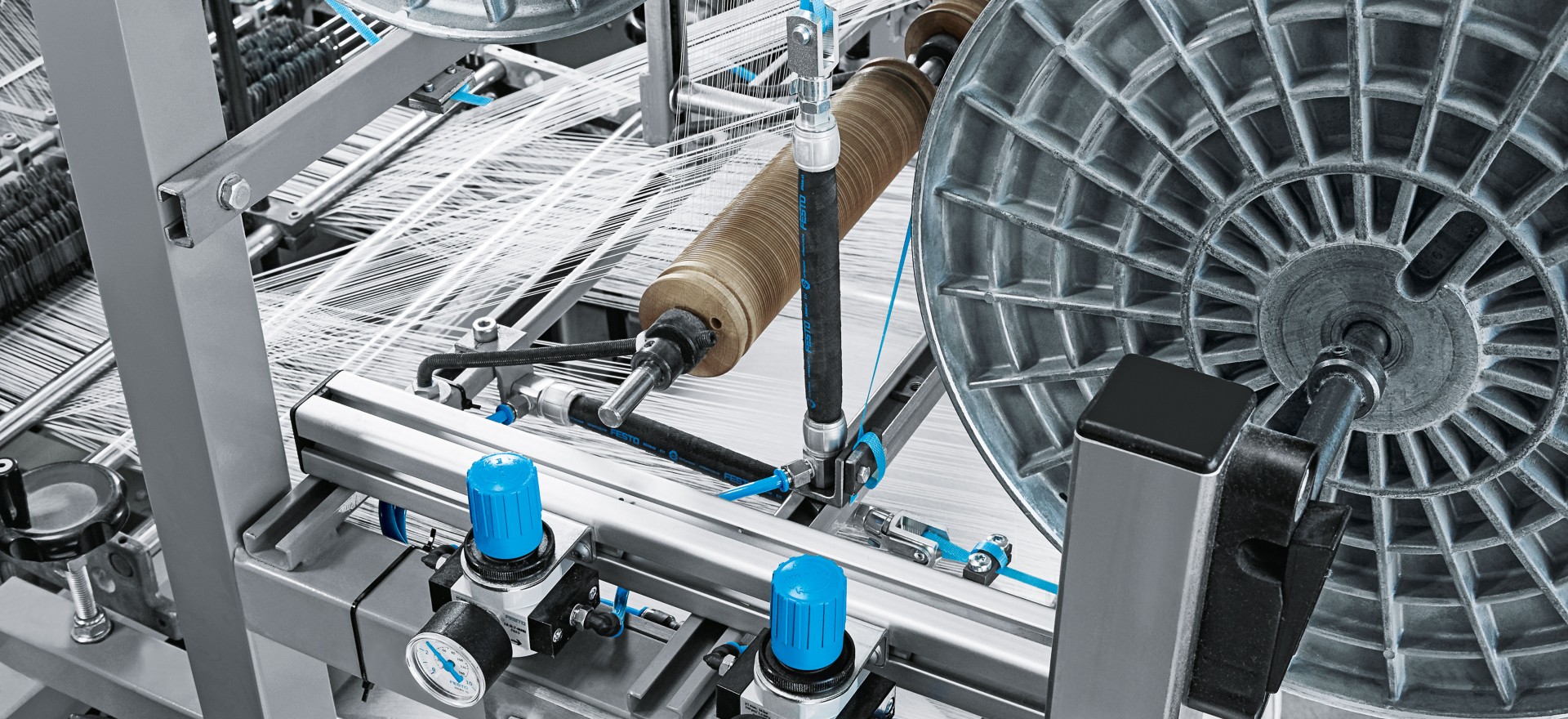
Future Trends in Textile Machinery
As the textile industry continues to evolve, the integration of cutting-edge technology into textile machinery has become a significant focus. The rapid pace of technological advancement presents numerous opportunities for efficiency, quality improvement, and sustainability. Below, we delve into key advancements reshaping the textile landscape and consider potential future directions for textile machinery.
Technological Advancements in Textile Industry
Modern textile machinery is increasingly characterized by automation, data analytics, and smart manufacturing processes. Here are some notable advancements:
- Automation: Automated textile machines significantly reduce human intervention, improving precision and speed. Machines can now handle repetitive tasks like weaving and sewing with unmatched efficiency.
- Data Analytics: The rise of IoT (Internet of Things) in textile machinery allows manufacturers to collect and analyze data in real time. This facilitates predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and reducing operational costs.
- 3D Knitting Technology: This innovative technique allows for the production of complex shapes and customized designs in a single process, making it easier to meet consumer demands for personalized products.
- Environmentally Friendly Practices: Many manufacturers are investing in machines that utilize less water and energy, as well as those that reduce emissions during production. This is driving the adoption of sustainable practices in the industry.
As a personal anecdote, visiting a textile expo recently showcased a revolutionary spinning machine that utilizes AI to monitor fiber quality continuously. This not only ensures consistent output but also reduces waste, highlighting how technology keeps pushing boundaries in textile manufacturing.
Predictions for the Future of Textile Machinery
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the future of textile machinery further. Here are some key predictions:
- Enhanced AI Integration: The use of artificial intelligence will not just simplify complex processes but will enable machines to learn from patterns in production, leading to intelligent decision-making.
- Customization at Scale: As consumer demand shifts toward personalized textiles, machinery capable of producing small batches of custom designs quickly and efficiently will become essential.
- Circular Economy Solutions: The future could see textile machines designed to facilitate the recycling of materials, reducing wastage and moving towards more sustainable production cycles.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: With advancements in connectivity, manufacturers will likely implement systems allowing for remote management of machinery, ensuring efficiency and troubleshooting without on-site presence.
In summary, the future of textile machinery is leaning heavily on technological advancements aimed at improving productivity, reducing waste, and enhancing sustainability. As the industry progresses, manufacturers must stay adaptable, embracing these innovations to remain competitive. The journey ahead for textile machinery promises not only to meet consumer needs but also to contribute positively to the environment, highlighting the potential for a more sustainable future in textiles.

